Economy
Top 10 Strongest Empire Of The History
Writeex
2024. 6. 7. 01:03
Ranking the greatest empires in history involves considering various factors such as territorial extent, military prowess, economic power, cultural influence, and longevity. Here’s a list of ten of the strongest empires, along with a brief overview of their achievements and contributions:
1. Roman Empire (27 BCE - 476 CE)
- Extent: At its peak under Emperor Trajan, the Roman Empire covered most of Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East.
- Military: The Roman legions were highly disciplined and used innovative strategies, such as the Testudo formation. Their engineering skills were evident in the construction of fortifications, roads, and bridges.
- Economy: The Romans built extensive trade networks across their empire, facilitating the movement of goods and resources. They were also known for their coinage system, which stabilized the economy.
- Culture: Roman law, language (Latin), and architecture have had a lasting impact on Western civilization. They built enduring structures such as the Colosseum, aqueducts, and the Roman Forum. Roman law principles, including concepts of justice and citizenship, have influenced modern legal systems.
- Governance: The Roman Republic and later the Empire developed complex administrative systems, including the Senate, various magistracies, and later imperial governance structures.

Achievements:
- Law and Governance: Developed a comprehensive legal system, including the Twelve Tables and the Corpus Juris Civilis, which influenced modern legal systems.
- Architecture and Engineering: Innovations such as the Colosseum, aqueducts, Roman roads, and monumental buildings like the Pantheon.
- Military Innovations: Disciplined legions, advanced military strategies, and construction of fortifications and defensive structures.
- Cultural Integration: Spread of Latin language, Roman culture, and citizenship across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East.
- Urban Planning: Development of advanced urban infrastructure, including public baths, amphitheaters, and forums.
2. Mongol Empire (1206 - 1368)
- Extent: The Mongol Empire stretched from Eastern Europe to the Sea of Japan, covering parts of Siberia, the Indian subcontinent, and the Middle East.
- Military: The Mongol military was known for its exceptional mobility, use of composite bows, and psychological warfare. Genghis Khan's strategies emphasized speed and surprise.
- Economy: The Pax Mongolica created a period of stability and law and order across Eurasia, facilitating trade along the Silk Road. This led to an exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies between East and West.
- Culture: The Mongols promoted religious tolerance and cultural exchange. They employed scholars and artisans from different parts of their empire, which led to a rich cultural synthesis.

Achievements:
- Pax Mongolica: Established a period of peace and stability across Eurasia, enhancing trade and cultural exchange on the Silk Road.
- Military Prowess: Revolutionary military tactics, including the use of composite bows, cavalry, and psychological warfare.
- Cultural Exchange: Promoted religious tolerance and exchange of knowledge, bringing together scholars and artisans from different regions.
- Administration: Implemented effective governance systems and communication networks, including the Yam postal system.
- Expansion: Created the largest contiguous land empire in history, uniting diverse cultures and regions.
3. British Empire (1583 - 1997)
- Extent: The British Empire was the largest in history, with colonies and territories on every inhabited continent, including significant portions of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and Oceania.
- Military: The Royal Navy was crucial in establishing and maintaining British dominance. Britain’s military prowess was demonstrated in conflicts such as the Napoleonic Wars and the World Wars.
- Economy: The British Empire played a key role in the Industrial Revolution, fostering technological advancements and global trade networks. The empire's economic policies and trade routes helped spread industrialization worldwide.
- Culture: English became a global language due to the British Empire. British legal and educational systems were established in many colonies. Cultural exports included literature, sports like cricket and football, and political ideas such as democracy and constitutional monarchy.

Achievements:
- Industrial Revolution: Led the world in technological advancements and industrialization, profoundly changing global economies.
- Global Trade Networks: Established extensive trade routes, including the triangular trade and the British East India Company.
- Cultural Influence: Spread of the English language, British legal systems, and educational models globally.
- Military Success: Key victories in the Napoleonic Wars, World War I, and World War II, establishing naval and military dominance.
- Scientific and Intellectual Contributions: Advancements in science, literature, and the arts, with figures like Isaac Newton and William Shakespeare.
4. Ottoman Empire (1299 - 1922)
- Extent: The Ottoman Empire covered Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa, including important cities like Istanbul, Cairo, and Baghdad.
- Military: The Ottomans were known for their effective use of gunpowder, their elite Janissary corps, and their naval power in the Mediterranean.
- Economy: The Ottomans controlled key trade routes between Europe and Asia. Their cities were bustling centers of commerce, culture, and learning. The use of the caravanserai system facilitated trade and travel.
- Culture: Ottoman architecture, like the Blue Mosque and Topkapi Palace, is renowned. They fostered a rich cultural life, including advancements in science, literature, and art. The millet system allowed for religious diversity within the empire.
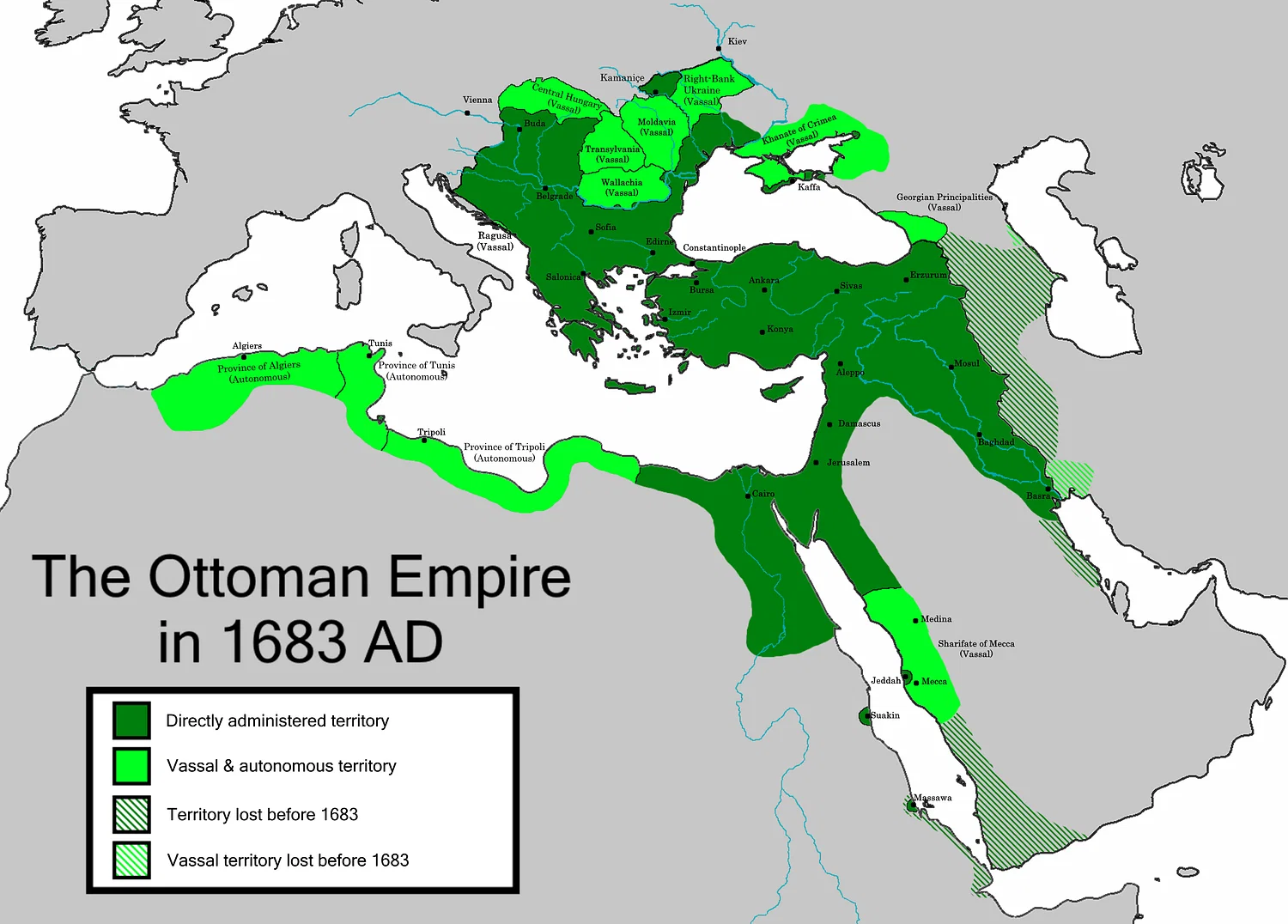
Achievements:
- Architectural Marvels: Construction of iconic buildings like the Blue Mosque, Topkapi Palace, and Hagia Sophia's transformation.
- Military Innovation: Effective use of gunpowder weapons, elite Janissary corps, and strong naval forces.
- Economic Prosperity: Controlled key trade routes, including the Silk Road and the Mediterranean, fostering economic growth.
- Cultural Synthesis: Fusion of Byzantine, Persian, Arab, and Turkish cultures, promoting advancements in art, literature, and science.
- Administrative Efficiency: Developed the millet system, allowing religious and cultural autonomy within the empire.
5. Russian Empire (1721 - 1917)
- Extent: The Russian Empire spanned Eastern Europe, Asia, and North America (including Alaska).
- Military: Russia had a formidable land army and an expanding navy. They participated in key conflicts like the Napoleonic Wars and the Crimean War.
- Economy: Russia’s economy was based on large-scale agriculture, vast natural resources, and later industrialization. The Trans-Siberian Railway epitomized the empire’s infrastructural advancements.
- Culture: The Russian Empire contributed significantly to world culture through its literature (Tolstoy, Dostoevsky), music (Tchaikovsky), and ballet. The Russian Orthodox Church also played a key role in cultural and social life.
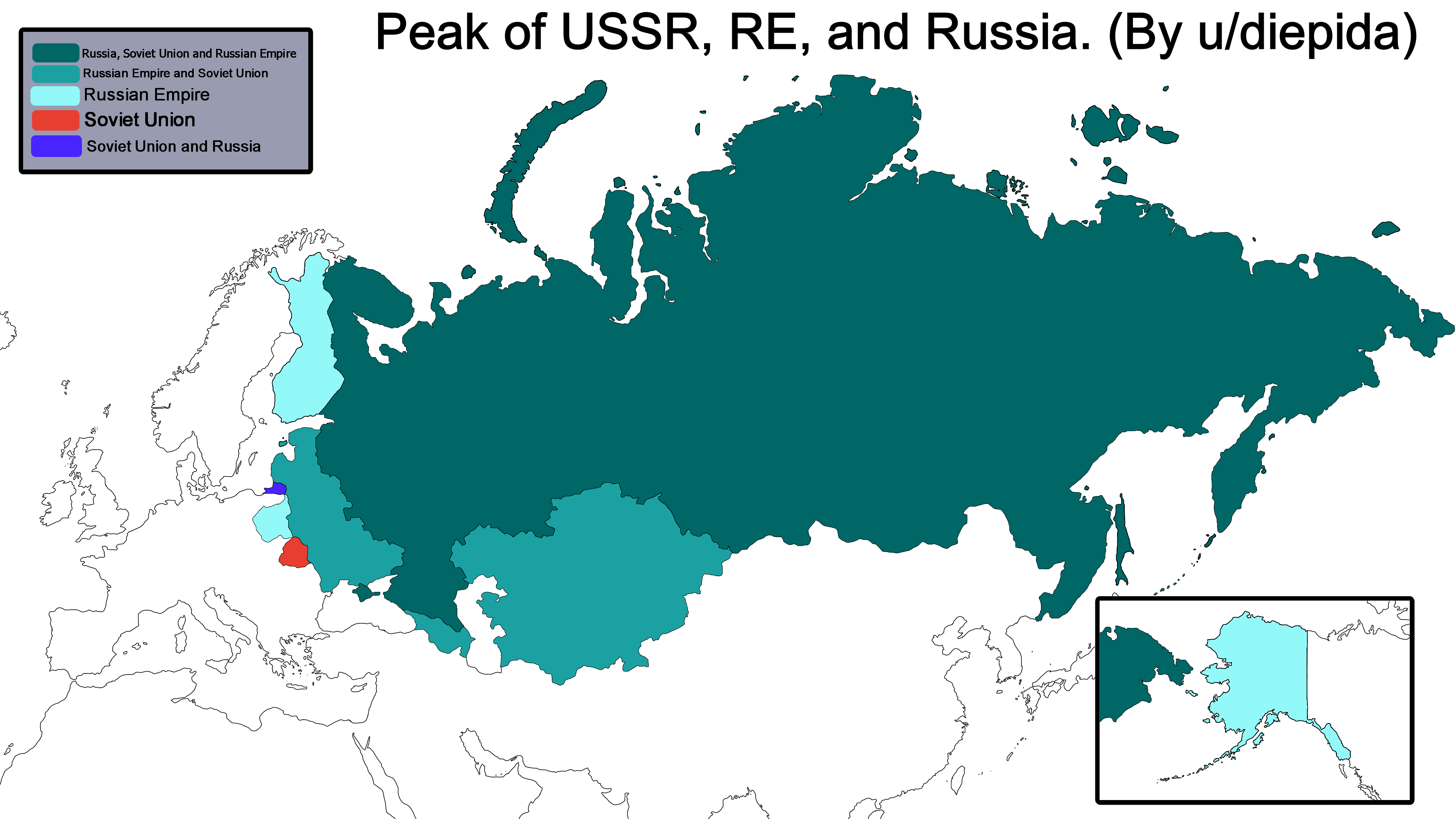
Achievements:
- Territorial Expansion: Expanded across Siberia to the Pacific Ocean and into Alaska, exploring and settling vast territories.
- Cultural Contributions: Flourishing of Russian literature, music, and ballet, with notable figures like Tolstoy, Dostoevsky, and Tchaikovsky.
- Economic Development: Significant agricultural output and industrialization in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
- Scientific Advancements: Contributions to science and technology, including space exploration foundations.
- Orthodox Christianity: Strengthening of the Russian Orthodox Church and its cultural and social influence.
6. Qing Dynasty (1644 - 1912)
- Extent: The Qing Dynasty ruled over China, Taiwan, Mongolia, Tibet, and parts of Central Asia.
- Military: The Qing maintained a strong centralized military and used advanced artillery and naval forces to expand and defend their empire.
- Economy: The Qing dynasty saw agricultural advancements and expanded trade both overland and via maritime routes. The empire’s economy was one of the largest and most complex in the world.
- Culture: Qing China was a period of significant cultural development, including advancements in painting, literature, and philosophy. The dynasty preserved traditional Chinese culture and Confucian values while also adopting and integrating new ideas and technologies.

Achievements:
- Cultural Preservation and Flourishing: Preservation of traditional Chinese culture and Confucianism, coupled with advancements in art, literature, and philosophy.
- Agricultural and Economic Growth: Agricultural innovations and expanded trade, including the Canton System regulating foreign trade.
- Military and Territorial Control: Maintained strong military presence and expanded territory to include Taiwan, Mongolia, Tibet, and Central Asia.
- Technological and Scientific Contributions: Advances in science and technology, including improvements in medicine and astronomy.
- Cultural Integration: Blended Manchu and Han Chinese cultures, promoting a unique and rich cultural synthesis.
7. Spanish Empire (1492 - 1976)
- Extent: The Spanish Empire included territories in the Americas, Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- Military: Spain’s powerful navy, exemplified by the Spanish Armada, enabled it to build and maintain a vast empire. They were pioneers in the Age of Exploration.
- Economy: Wealth from silver and gold mines in the Americas fueled the Spanish economy and funded its European ambitions. Spain established extensive trade networks, including the Manila galleons that connected Asia with the Americas.
- Culture: The Spanish Empire spread Christianity, the Spanish language, and Iberian culture worldwide. They left a lasting legacy in architecture, art, and urban planning in the Americas.

Achievements:
- Age of Exploration: Pioneered global exploration with figures like Christopher Columbus, leading to the discovery of the New World.
- Wealth from Colonies: Exploited vast resources from the Americas, including gold and silver, fueling European economies.
- Cultural and Religious Influence: Spread of Catholicism, Spanish language, and Iberian culture across the Americas and Asia.
- Architectural and Urban Developments: Built iconic cities and structures in the Americas, such as Mexico City and Lima.
- Scientific and Navigational Advances: Contributions to cartography, navigation, and maritime technology.
8. Umayyad Caliphate (661 - 750)
- Extent: The Umayyad Caliphate stretched from the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Indus River in the east.
- Military: The Umayyads rapidly expanded through disciplined armies and effective military strategies, creating a vast and diverse empire.
- Economy: They developed a robust economy based on trade across the Mediterranean, Silk Road, and Indian Ocean. The introduction of a unified coinage system facilitated commerce.
- Culture: The Umayyads built architectural marvels like the Great Mosque of Damascus and the Alhambra. They also fostered the development of science, philosophy, and medicine, blending Greek, Persian, and Indian influences.

Achievements:
- Rapid Expansion: Created one of the largest empires in history, spanning from Spain to India in a relatively short period.
- Cultural and Scientific Flourishing: Promoted the translation and preservation of Greek, Persian, and Indian knowledge, contributing to the Islamic Golden Age.
- Architectural Achievements: Constructed significant buildings, including the Great Mosque of Damascus and the Alhambra.
- Economic Integration: Unified the economy with standardized coinage and promoted trade across the empire.
- Religious and Administrative Innovations: Developed efficient administrative structures and policies of religious tolerance.
9. French Colonial Empire (16th century - 20th century)
- Extent: The French Empire included territories in North America, the Caribbean, Africa, Asia, and the Pacific.
- Military: France had strong land forces and naval capabilities, which were crucial in their colonial conquests and in key conflicts like the Napoleonic Wars.
- Economy: French colonies produced valuable commodities such as sugar, coffee, spices, and more. France established extensive trade networks and exploited colonial resources for economic gain.
- Culture: The French Empire spread the French language, legal systems, and education models. The ideas of the French Revolution influenced colonial governance and inspired movements for independence.
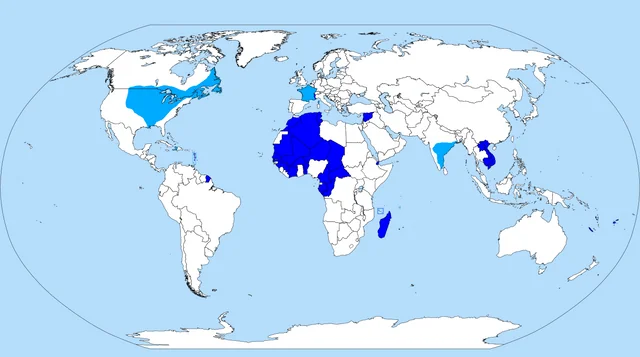
Achievements:
- Cultural Influence: Spread French language, legal systems, and education models to colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
- Economic Exploitation and Development: Developed profitable plantations and resource extraction industries in colonies.
- Military and Naval Prowess: Strong military forces and significant naval battles, especially during the Napoleonic Wars.
- Scientific and Intellectual Contributions: Promoted Enlightenment ideas and advancements in science, philosophy, and arts.
- Architectural and Urban Planning: Built French-style cities and infrastructure in colonies, influencing local architecture and urban design.
10. Achaemenid Empire (550 - 330 BCE)
- Extent: The Achaemenid Empire, founded by Cyrus the Great, covered a vast area from the Balkans and Eastern Europe to the Indus Valley.
- Military: The empire had large and diverse armies, advanced logistics, and employed effective strategies. Notable battles include those against the Greeks.
- Economy: The Achaemenid Empire had extensive trade networks and introduced standardized coinage. They built impressive infrastructure, including the Royal Road, which facilitated communication and trade.
- Culture: The Achaemenids practiced religious tolerance, respecting local customs and religions. They constructed monumental architecture, such as Persepolis, and contributed to administrative and governance practices that influenced future empires.

Achievements:
- Administrative Innovations: Developed the satrapy system for efficient regional governance and the Royal Road for communication and trade.
- Cultural and Religious Tolerance: Respected local customs and religions, promoting stability and cultural diversity within the empire.
- Architectural and Engineering Feats: Constructed monumental structures like Persepolis and impressive engineering projects.
- Economic Prosperity: Created extensive trade networks, standardized coinage, and promoted economic integration across the empire.
- Military Successes: Built a powerful and diverse army, successfully conquering vast territories and defending the empire against external threats.