Insurance is a fundamental part of our financial safety net, providing a shield against unexpected losses and uncertainties. But behind the protection offered by insurance policies lies a complex framework of laws and regulations. These laws ensure that insurance companies operate fairly and that policyholders are protected. This guide delves into the intricate world of insurance laws, covering their purpose, types, key principles, and notable regulations.

1. The Purpose of Insurance Laws
Insurance laws serve several critical functions:
- Consumer Protection: Safeguarding policyholders from unfair practices and ensuring they receive fair treatment and prompt payouts.
- Market Stability: Maintaining the financial solvency of insurance companies to prevent industry collapse.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring companies adhere to established standards and ethical practices.
- Fair Competition: Promoting a competitive marketplace where no entity has an undue advantage.
2. Types of Insurance Laws
Insurance laws can be broadly categorized into several types:
a. Contract Law
Insurance is fundamentally a contract between the insurer and the insured. This segment of law governs the terms, conditions, and obligations stipulated in insurance policies. Key aspects include:
- Formation of Contract: Valid offer and acceptance, consideration, and legal purpose.
- Policy Terms and Conditions: Coverage limits, exclusions, and riders.
- Claim Settlement: Procedures and timeframes for filing and settling claims.
b. Regulatory Law
These laws oversee the operations of insurance companies and the industry as a whole. They ensure companies maintain solvency, adhere to ethical practices, and protect consumer interests. Important areas include:
- Licensing and Authorization: Requirements for companies to operate within a jurisdiction.
- Solvency Regulations: Capital and reserve requirements to ensure companies can meet their obligations.
- Rate Regulation: Approval and monitoring of the premiums charged to policyholders.
c. Tort Law
This area deals with civil wrongs where one party's negligence causes harm to another. In insurance, it often relates to:
- Liability Insurance: Policies that cover damages or injuries caused to others (e.g., auto or general liability insurance).
- Bad Faith Claims: Legal claims against insurers for unfair or deceptive practices.
d. Consumer Protection Law
These laws are designed to protect policyholders from unfair practices by insurance companies. They cover:
- Disclosure Requirements: Ensuring clear communication of policy terms and conditions.
- Claims Handling: Standards for the timely and fair processing of claims.
- Unfair Practices: Banning misleading advertising, discrimination, and unfair denial of claims.
3. Key Principles of Insurance Law
Several core principles underpin the functioning of insurance laws:
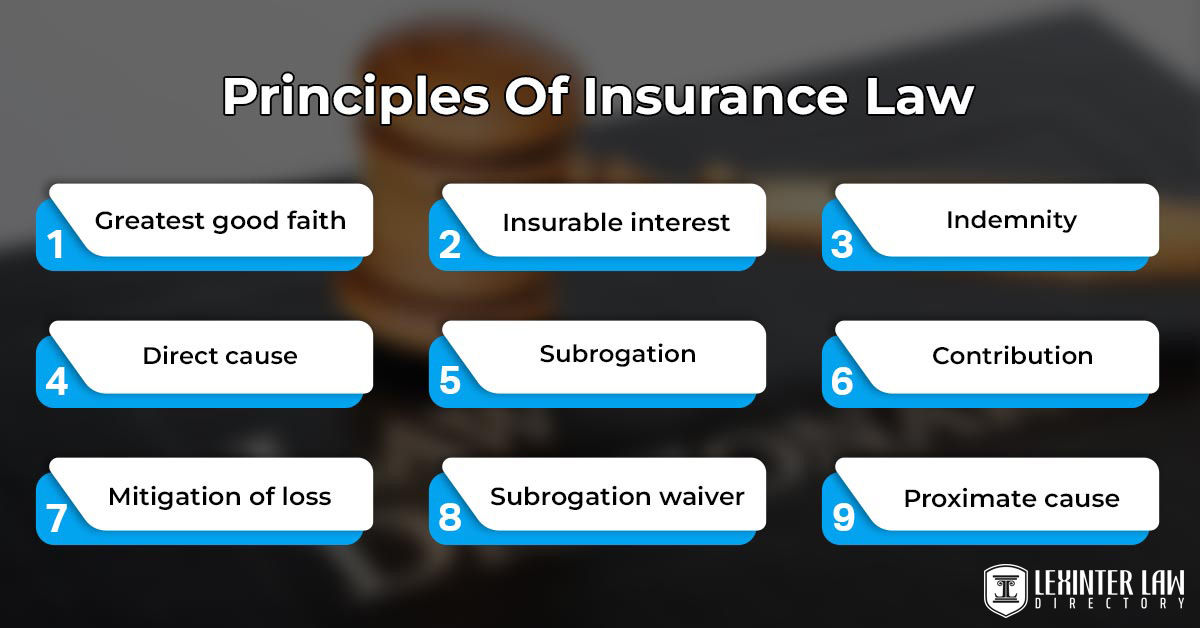
a. Principle of Utmost Good Faith (Uberrimae Fidei)
This principle requires both parties to an insurance contract to act honestly and disclose all relevant facts. The insurer must provide clear and complete information about the policy, and the insured must disclose all material information that could affect the risk.
b. Principle of Insurable Interest
An insured must have a legitimate interest in the subject matter of the insurance, meaning they would suffer a financial loss or some other type of harm if the insured event occurs. This principle ensures that insurance is not used for speculative purposes.
c. Principle of Indemnity
Insurance policies are designed to restore the insured to their financial position before the loss, not to enable them to profit from the insurance. This principle limits payouts to the actual amount of loss incurred.
d. Principle of Contribution
If an insured has multiple policies covering the same risk, this principle ensures that they can only recover the proportional amount of the loss from each policy, preventing double recovery.
e. Principle of Subrogation
After compensating the insured for a loss, the insurer gains the right to pursue any third party that caused the loss to recover the amount paid out.
4. Notable Insurance Regulations
a. The McCarran-Ferguson Act (1945) - USA
This Act grants individual states the authority to regulate insurance, exempting the industry from most federal antitrust laws. It underscores the importance of state regulation and the protection of local consumer interests.
b. Solvency II Directive - European Union
This regulatory framework governs the amount of capital that EU insurance companies must hold to reduce the risk of insolvency. It aims to unify the insurance market and enhance consumer protection through stringent financial requirements and risk management practices.
c. General Insurance Code of Practice - Australia
This Code sets standards for general insurers regarding sales, service, claims handling, and dispute resolution. It promotes transparency, fairness, and accountability within the industry.
5. Emerging Trends in Insurance Law
The insurance landscape is constantly evolving, influenced by technological advancements and socio-economic changes. Key emerging trends include:
a. Cyber Insurance and Data Protection
With the rise in cyber threats, laws governing cyber insurance and data protection are becoming crucial. Policies must adapt to cover losses from data breaches, ransomware, and other cyber risks, while regulations ensure companies protect sensitive information.
b. Climate Change and Environmental Liability
As climate change intensifies, insurance laws are expanding to address environmental risks. This includes coverage for natural disasters and liability for environmental damage.
c. Insurtech and Digital Transformation
The integration of technology in insurance, or 'Insurtech,' is reshaping the industry. Laws are evolving to address issues related to digital platforms, online policy purchases, and automated claims processing.
6. Conclusion
Insurance laws are vital to maintaining a balanced, fair, and secure insurance market. They protect consumers, ensure company solvency, and promote ethical practices. As the world changes, these laws must evolve to address new challenges and opportunities, ensuring the industry continues to serve its essential role in society.
Further Reading and References
- Books:
- Insurance Law and Regulation by Kenneth S. Abraham.
- Principles of Insurance Law by Jeffrey W. Stempel.
- Online Resources:
For a deep dive into the specifics of insurance law in your jurisdiction, consult your local regulatory bodies or legal experts specializing in insurance law.
'Educational' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Essential Checklist : What to Consider Before Buying Insurance (0) | 2024.06.09 |
|---|---|
| What Is Insurance And Its Types (2) | 2024.06.09 |